Through the use of ” AQL tables” a company sourcing from a factory can evaluate:
Click here to learn more
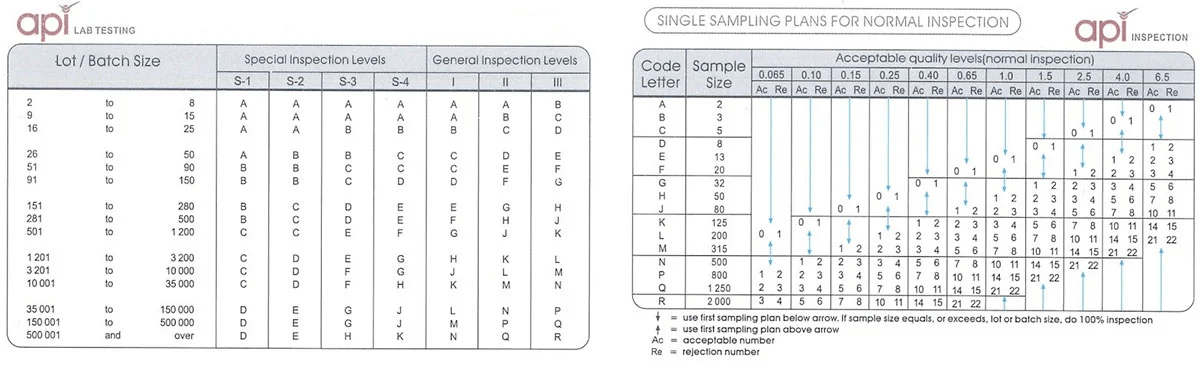
A production batch will systematically contain defective products. Even after factory quality control assessment and repairs have been performed, some defects will remain. The buyer can only accept a certain level of non-quality and should refuse any lot which contains too many instances of non conformity. As such, buyers need to be able to define what constitutes an acceptable quantity of defective products, as well as the types of non-quality that can be considered acceptable. AQL tables have been designed to define this level of acceptable non-quality.
Table 1: An Example of an AQL table:
Certification is the formal procedure by which an accredited or authorized person or agency assesses and verifies (and attests in writing by issuing a certificate) the attributes, characteristics, quality, qualification, or status of individuals or organizations, goods or solutions, procedures or processes, or events or situations, in accordance with established requirements or standards. ( Source:The Business Dictionary)
Notification is an act whereby a Member State informs the Commission and the other Member States that a body, which fulfils the relevant requirements, has been designated to carry out conformity assessment according to a directive. Notification of Notified Bodies and their withdrawal are the responsibility of the notifying Member State (Source: EU website).
Accreditation is a quality infrastructure tool which supports the credibility and value of the work carried out by conformity assessment bodies and thus of the corresponding attestations issued by them (test and inspection reports, calibration certificates, certifications of management systems, products and personnel and other attestations). Accreditation of conformity assessment bodies is carried out against globally accepted requirements set out in international standards defining competence criteria for the category of conformity assessment body, against supplementary sector specific requirements and against guidance documents from international and regional cooperation organisations of accreditation bodies. A product or service accompanied by a conformity attestation delivered by an accredited conformity assessment body inspires trust as to the compliance with applicable specified requirements. Thereby accreditation favours the elimination of technical barriers to trade. (Source: EU website).
By affixing the CE marking on a product, the manufacturer declares on his/her sole responsibility that the product is in conformity with the essential requirements of the directives that apply to it and that the relevant conformity assessment procedures have been fulfilled. Thus products bearing the CE marking benefit from free circulation in the European Market.( source: EU Website ).
Learn more about CE marking.
CSR refers to the concept whereby companies integrate social and environmental concerns in their business operations and in their interaction with stakeholders on a voluntary basis. Companies which have integrated the concept of CSR behave ethically and contribute to economic development while improving the quality of life of the workforce and their families, as well as of the local community and society at large.
RAPEX is the EU rapid alert system for all dangerous consumer products, with the exception of food, pharmaceutical and medical devices. It allows for the rapid exchange of information between Member States and the Commission via central contact points (the National Contact Points ) regarding measures taken to prevent or restrict the marketing or use of products posing a serious risk to the health and safety of consumers. Both measures ordered by national authorities and measures taken voluntarily by producers and distributors are covered by RAPEX. (Source: EU website).
The Regulation links up national, public enforcement authorities in an EU-wide Enforcement Network which has been given the means to exchange information and to work together to stop rogue traders or any other cross-border breach to consumer protection laws. All the authorities in the Network have similar investigation and enforcement powers which include the possibility of carrying out on-site inspections.
Public enforcement authorities in the Member States play a decisive role in ensuring that consumer protection laws are correctly enforced. The Enforcement Network formally started its operations end of 2006.
Read more on the EU Website.

Want to know more about one of our many services? Contact us to find out more information about what API can do for your company today.
Address
Copyright © 1981 – 2022 API. All Rights Reserved.